Recognizing Gluten Sensitivity: Top 10 Warning Signs
Gluten can sneakily trigger health problems without clear indications. Understanding how your body reacts to it is crucial for maintaining well-being, especially since its effects often go unnoticed yet cause long-term harm.
1. Digestive Disturbances
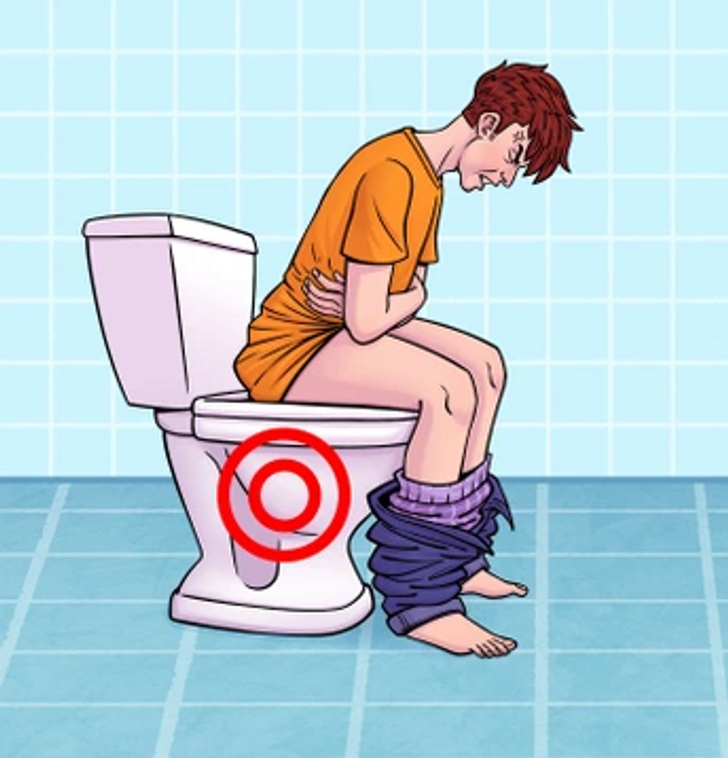

If you’re experiencing nausea, bloating, or abdominal pain, there might be a gluten connection—often these issues are mistaken for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Many dealing with IBS might actually have gluten sensitivity, creating a barrier to getting the right treatment.
2. Unexplained Weight Shifts
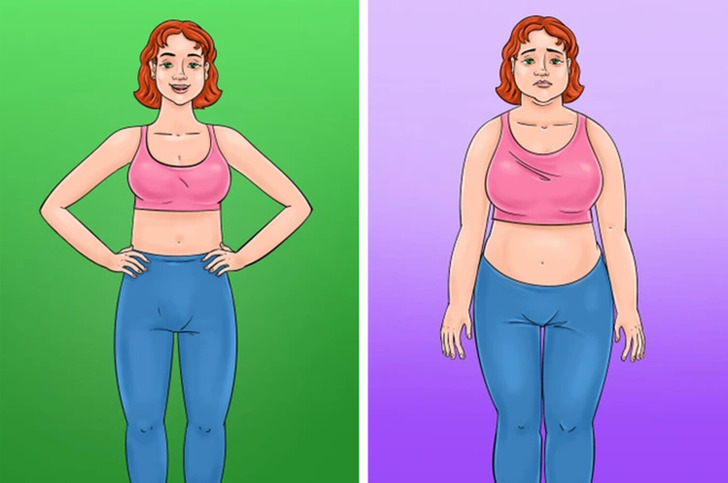

Seeing your weight fluctuate unexpectedly might be troubling, but it can be a sign of gluten sensitivity. Inflammation and metabolic issues often cause this, and if you have other nutrient absorption troubles, it might be worth investigating gluten intolerance.
3. Hormonal Imbalances

Unexpected weight changes, sleeplessness, and irregular menstrual cycles might stem from gluten intolerance. These hormonal shifts, more common in women, can become increasingly noticeable during key life phases like menopause.
4. Neurological and Psychological Symptoms
Struggling with concentration, feeling anxious, or experiencing brain fog might be linked to gluten-induced inflammation. Moreover, migraines occurring soon after eating can signal sensitivity to gluten.
5. Skin and Nail Challenges
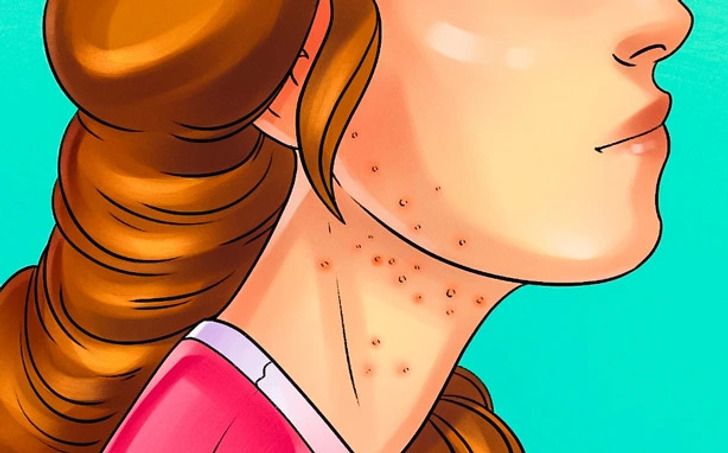

Itchy and persistent rashes could indicate gluten intolerance, often linked to conditions like eczema. Nail brittleness is another sign, potentially arising from gluten’s interference with nutrient absorption.
6. ADHD Symptoms
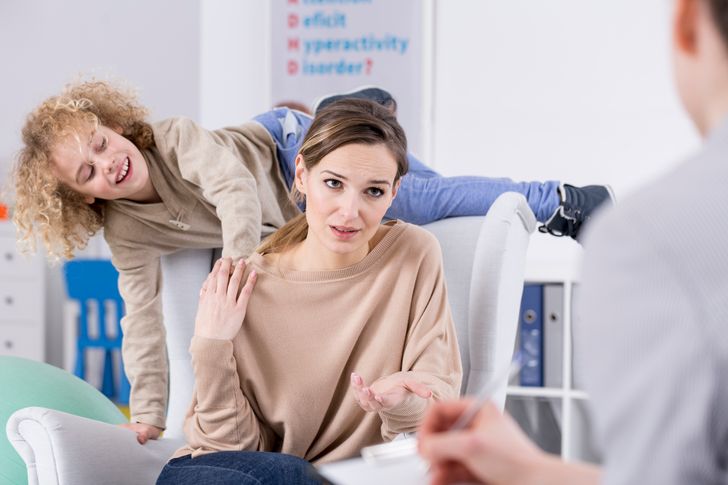

Lasting attention issues in adults and children might be relieved with a gluten-free diet. This can mitigate symptoms tied to Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder.
7. Dental Health Concerns
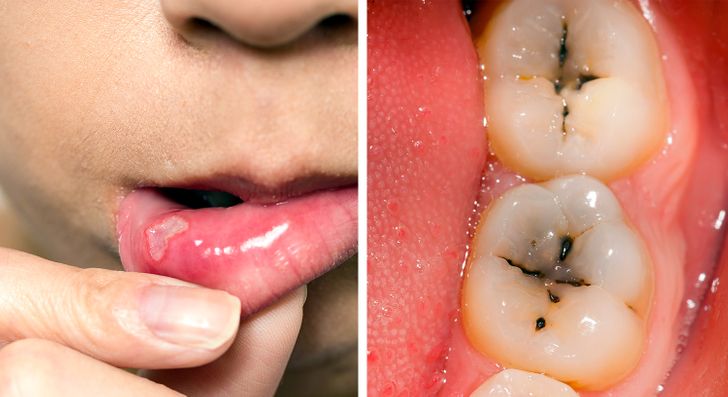
Maintaining dental health can be challenging if gluten sensitivity is impacting nutrient absorption, leading to enamel problems and cavities despite excellent oral hygiene practices.
8. Iron Deficiency Anemia
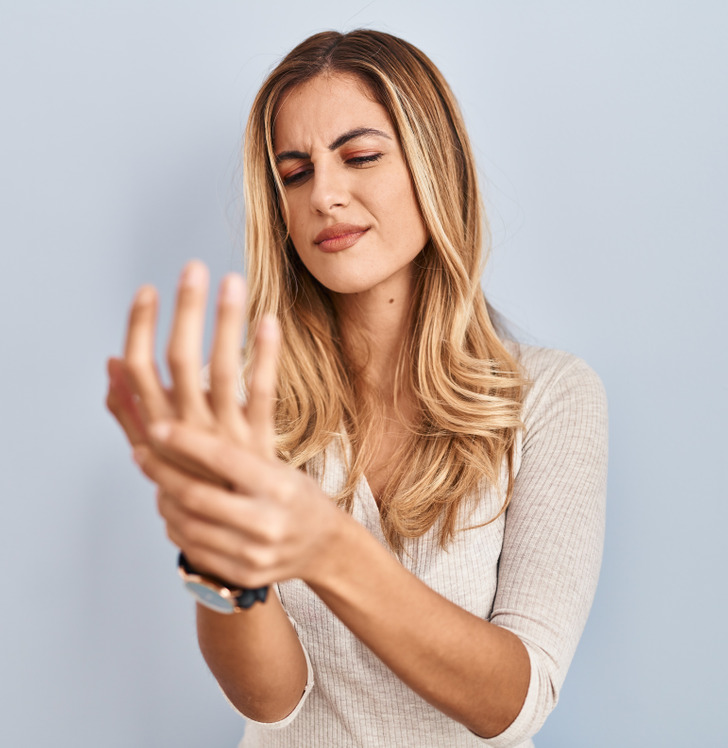

Persistent fatigue or pale skin might result from iron-deficiency anemia, a common celiac disease indicator, due to gluten inhibiting iron absorption.
9. Autoimmune Disorders
Many with gluten intolerance develop celiac disease, an autoimmune condition. This diagnosis can raise risks of other autoimmune ailments, complicating health management further.
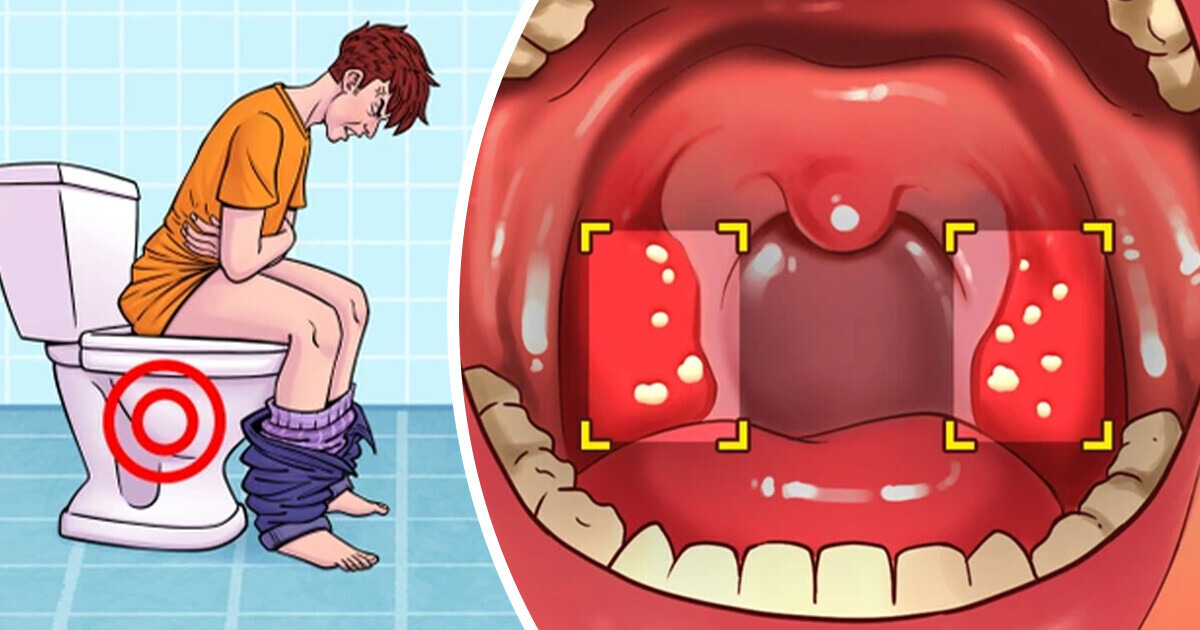
10. Tonsil Stones
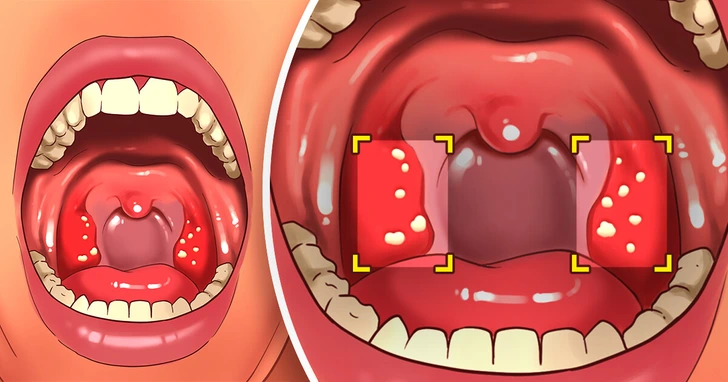
Though research is limited, there may be associations between gluten sensitivity and tonsil stones, with dietary changes possibly providing relief from this uncomfortable issue.
Managing Gluten Sensitivity

1. Testing is Key: Consult your physician to test for antibodies associated with celiac disease. Ensure your diet includes gluten pre-test for accurate results.
2. Dietary Adjustments: Avoid foods containing gluten by reading labels carefully and opting for gluten-free choices to alleviate symptoms and promote overall health.